
The bulk of the cells of the usual nesting honeycomb make up the bee cells. They have a hexagonal shape and serve to educate the larvae of working bees, as well as the folding of honey and perga.
The trout cells also have a hexagonal shape, but are much larger in size. In them bees raise larvae of drones, add honey and extremely rarely – pergus.
The transition cells have an irregular shape. Bees rebuild them in places of transition from bee cells to drones.
The marginal cells also have an irregular shape. With their help, bees attach the honeycomb to the borders of the frame.
Honey cells resemble bees in shape, but differ in their depth and appreciable slope of the walls upwards. They are usually located at the top of the honeycomb honeycomb frame (especially with an extended street) or occupy the entire area of the store frame.
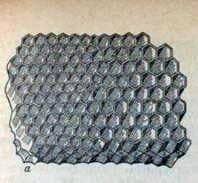
Fig. Wax constructions of bees: 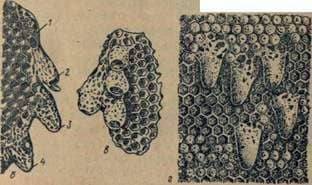 A – cells of bees (left), drone (right), honey (in the center);
A – cells of bees (left), drone (right), honey (in the center);
B – swarming queen cells: 1 – bowl
(base of the mother liquor); 2 – mother after the exit of the uterus; 3-sealed mother fruit pot; 4 – gnawed bees (destroyed) motherhood;
C – bowls on honeycombs;
G – sealed fistula cells on a honeycomb with brood
The queen cells are special cells, resembling an acorn or a truncated cone in appearance. They serve for the withdrawal of queens. There are 2 types of queen cells: swarm and fistulous.
Royal queen cells appear when the family enters a swarm condition. Bees lay them on the rib, the bottom edge or along the edges of large honeycomb holes. The beginning of the queen cell with a round bottom and thick walls is called a bowl.
Fistullary queen bees lays when a sudden death of the uterus. In this case, the base of the queen cell is an ordinary bee cell with a larva of one, two days old already present there.
Пыльцеуловитель своими руками. Пыльца в соте.
Wax and its classification