Sick brood – an infectious disease, a viral etiology, causing the death of adults often sealed larvae and young pupae.
The body of the dead larvae takes the form of a bag of liquid.
The economic damage is small. The disease is rare, often self-healing.
The causative agent of the disease is the filtering virus Moga-torvirus aetatulae Holmes. The virus passes through the bacterial filters of Seitz, Berkefeld, Pasteur-Schamberlan.
The virus of saccular brood in water dies at 59 њ for 10 minutes, and in honey or glycerin at 70-73 њ – for 10 minutes. At room temperature, it persists in the dried state for about three weeks. By direct sunlight the dried virus is killed within 4-7 hours, the virus weighed in water dies within 4-6 hours, weighed in honey – in 5-6 hours. In diffused light at room temperature, the virus persists in honey for about a month. At room temperature in a 10% fermentation solution of sugar syrup, the virus dies within 3-5 days; in conditions of putrefaction, the virus persists for 7-10 days and in a 1-2% solution of phenol – about three weeks.
Epizootic data. The virus is pathogenic for 5-6 day old bee larvae. Adult bees are ill with a viral disease in a latent form. In the body of adult bees, the virus persists throughout the winter until next year, when brood reappears. For humans and warm-blooded animals, the virus is harmless.
The spread of the disease in the family goes with the feeding of larvae with infected food (honey, pergus). Intra-bee-bees, cleaning cells and removing corpses, contaminate the mouth with mouthfuls, become infected, become virus carriers and infect them when feeding larvae. Adult bees, being virus carriers, spread the disease to other families of their own and neighboring apiaries.
Symptoms and course of the disease. The honeycomb with the affected brood has a mottled appearance, as it is with rotting diseases. The cells of the cells are partially removed or perforated. Bends mainly printed brood. Larvae of worker bees, drones and queens can be ill. There is no specific smell.
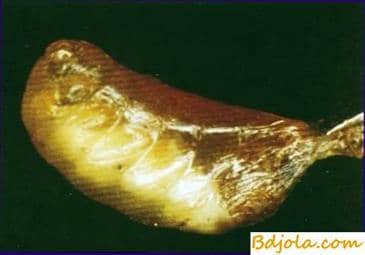
The color of the larvae becomes brownish. Corpses are easily removed from the cells. They look like a bag of liquid. When the skin ruptures, a granular mass emerges. Drying, the corpses wrinkle and take the form of a curved crust. Their heads are raised, and they take the form of a gondola.
The disease appears in May, June. In July, it is less common when there is a copious bribe, the disease fades out, and sometimes it stops. Negative external factors – long rains, cold snaps, absence of a bribe are conducive conditions.
Diagnosis. When microscopic examination with a light microscope of smears from pathological material (corpses of larvae, crusts), microorganisms are not found. A negative result is also given by bacteriological research.
Signs such as the lack of viscousness of rotting mass, specific smell, easy separation of dried corpses (crusts) and the absence of bacteria in microscopy, make it possible to differentiate the disease of saccule brood from foulbroods. With the brood brood, the larvae perish successively on the entire honeycomb, whereas in the case of saccule brood, as in the case of foulbroods, the lesion has a mottled appearance.
Prevention. On the apiaries contain strong families, they are provided with sufficient quantities of honey and perga, renew the nests, do not allow closely related breeding, systematically carry out the disinfection of beekeeping equipment.
Control measures. On the apiary, quarantine is imposed until the disease is completely eliminated. In sick families, the laying of eggs by the uterus is interrupted. For this, the sick uterus is enclosed in a cell for 5-7 days or more. Later, these queens are replaced, since they usually sharply reduce their egg production. From the specific means for the prevention of the disease, it is suggested to feed biomycin or levomycetin 50 mg per 1 liter of 50% sugar syrup. If the family is severely affected, then honeycomb with the affected brood is selected, they are replaced by honeycombs with a sealed brood from healthy families. Good results are provided by the introduction of swarms. Weak sick families connect.
In the event of a severe defeat, the families are transplanted into decontaminated beehives into frames waxed with artificial wax.
Приготовить рис с медом. Палатка передвижная.
Diseases of bees