American foulbrood

American foulbrood (malignant foulbrood, printed foulbrood) is an infectious disease of bee colonies, which causes their weakening and death as a result of decay of bee larvae at the age of pupation.
American foulbrood is found in all countries of the world where beekeeping is developed. In the subtropics and tropics, the disease is more common than in the more northern zones.
Economic damage. At large apiaries in the absence of recreational activities, American foulbrood quickly spreads and causes great losses. Each sick bee family collects honey 20-80% less healthy and dies within 2-3 years.
The causative agent of the disease, Bacillus larvae, is a straight sticks 2-5 microns long and 0.5-0.8 microns wide. The microbe is mobile. When staining with nigrosine or with negative coloring of ink on the preparation, flagella spirochetoobraznoy forms are visible. You. larvae gram-positive, it is painted with usual paints. The microbe forms spores of an oval shape measuring 1.2-1.8x 0.6-0.7 microns.
You. larvae grows on special serum media under aerobic conditions at 35-37 њ, medium pH 6.0-7.2, optimum 6.8. The microbe forms grayish-white overlays, which then become colorless. Overlays have uneven edges of the fibrous structure. After 24-28 hours, the colonies become visible with a slight increase. After two days, the growth is noticeable to the naked eye.
You. larvae indole does not form, gives traces of hydrogen sulphide, splits glucose, does not split mannitol, galactose, sucrose. The causative agent from different regions and countries has the same antigenic structure; when exposed to a bacteriophage, the microbe dissociates from typical R-forms to atypical S-forms; forms antigens: flagellate, somatic and sporic; has antibiotic properties. In its development, it suppresses the growth of other microbes.
In smears from pathological material (putrefactive mass of
Stability of the pathogen is high. In cultures, disputes persist for dozens of years. In honey, sunlight spores persist for 4 to 6 weeks. A 10% formalin solution kills spores after 6 hours. In cells with honey with the remains of dried corpse (crusts) you. larvae shows great stability.
Sulema 1: 1000 kills the spores in 5 days. In water, spores of the microbe die at 90 њ for 3 hours, at 100 њ after 13 minutes. Boiling honey kills spores for 40 minutes. Boiling honey with water at 1: 1 dilution kills spores for 20 minutes.
Epizootic data. Only adult larvae of worker bees and queens are affected by the American foulbrood, and rarely by drones. For humans and warm-blooded animals, the pathogen is harmless.
To infect one bee larva, no less than 10 000 spores in 0.01 ml of syrup are required.
The vegetative form of the pathogen can not cause infection. The source of the infection is a sick family. About 5 billion microorganisms multiply in the body of one diseased and dead larva.
In the bee family, the infection is spread by bees-nurses and bees-cleaners. They infect honey. From family to family, the infection is carried by bees-thieves. Important in the transfer of infection parasites of bees (wax moth, ham, mites), which, eating spores contaminated with wax, can mechanically tolerate the pathogen.
Infection can be transferred with careless work in the apiary (rearrangement of honeycomb frames from sick families to healthy ones, feeding contaminated with honey spores, use of non-disinfected equipment), while selling honey on the honey market from sick families.
The course and symptoms of the disease. The incubation period lasts 3-7 days. At the beginning of the disease, only single lesions of the larvae are found, then the number increases.
In a healthy family, brood, as a rule, is single-aged and occupies all the cells on the honeycomb. In a family affected by foulbrood, brood variegated. Cells with healthy larvae alternate with the diseased; brood of different ages: cells with a printed brood lie next to young larvae.
The lids of the cells above the dead larvae are darkened, perforated, slightly squeezed.
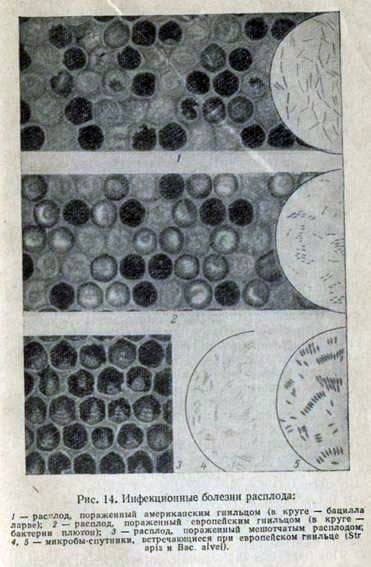
In the initial stage of the disease, the larva loses segmentation of the body, the pearl luster disappears, the body color of the larva becomes grayish-whitish, then turns into grayish brown. The skin of the larva is thinned, easily torn; When the process develops around the fourth week of illness, the larva becomes dark-coffee-colored. Fabrics are decomposed, turning into a sticky, stretching mass of dark-coffee color. This mass lies on the lower side wall of the cell, covering its entire length. If you open the cell in which the rotting mass is located and touch it with a bacteriological loop, then the mass stretches behind the loop with a thin, silky thread 10-15 cm long. The rotting mass of the larva resembles the smell of carpentry glue.
After a month, rotting larvae dry up and form crusts that tightly attach to the side walls of the cells, so that the bees can not remove them. The contagious beginning remains in the family and accumulates. Only single families, who have the ability to quickly and thoroughly clean cells, are able at the beginning of the disease to recover.
Diagnosis.

The described clinical symptoms, namely: the discord of the brood, the death of the printed brood, the stringency of putrefaction, the smell of carpentry glue from rotting larvae make it possible to diagnose the disease.
In determining the disease, this species of foulbrood should be differentiated from brood disease by European foulbrood. When European foulbrood is sick and die open brood, when the larvae are in the form of a ringlet, the bodies of the larvae are displaced from their places and have a yellowish color. Rotting mass does not possess the property of viscousness. A mixed infection is possible. Additional bacteriological and serological studies confirm the clinical diagnosis when detected in smears from tissues and in pure cultures of you. larvae.
Prevention. Healthy apiaries are protected from drift of the pathogen. Systematically conduct disinfection of apiary equipment and buildings, maintain the purity of the apiary. You can not use non-disinfected equipment obtained from other apiaries, you should not use an artificial wax obtained from apiaries, affected by foulbrood, or an artificial wax made from rotting raw materials in its artisanal production.
Control measures. If a disease is detected, immediately inspect the entire apiary to identify sick families, take samples of honeycombs with the affected brood and send them to the laboratory to clarify the diagnosis.
On the apiary, quarantine is imposed until the disease is completely eliminated.
If a fresh case of skidding of the American foulbrood is discovered, all the families in which the disease will be found are subject to destruction. Bees are killed by sulfur dioxide, ether or formalin. Honeycombs with frames and dead bees are burned.
Sometimes families are distilled into new or disinfected beehives into frames with strips of artificial wax and are treated. Overtake at the end of the day, preferably with a bribe. The bees are shaken on a piece of paper, spread out before the empty beehive, and they are guided by smoke into the ice. Paper after the distillation is burned, and honeycombs from sick families are immediately removed to a place inaccessible to bees. The uterus does not change. A week later put frames with whole sheets of artificial wax and expand the nest as needed.
Treatment. Prepare a therapeutic food, consisting of 2 parts of sugar and 1 part of water. Initially, establish how much sugar and syrup you need. Sugar is added to the hot water, which with constant stirring is brought to a boil. After cooling the syrup to 30 њ, one of the following medicines is added to it per liter: biomycin – 200-500 thousand units, terramycin – 500 thousand units, tetracycline 500 thousand units, streptomycin – 500 thousand units, nosulfazol sodium – 1 g, sulfantrol – 2 g. The finished medicinal syrup is given at the end of the day to each sick family of 100-150 ml per lane. The medicinal food is poured into feeding troughs or nesting honeycombs and put in beehives.
The nest is well insulated, the cracks in the beehive are closed, the flaps are cut, preventing the theft of bees.
The therapeutic syrup is given 3-4 times 5-7 days before complete recovery. Therapeutic top dressing is fed to the unfavorable apiary and uncared for families with a preventive purpose.
Disinfection. When American foulbrood is thoroughly disinfected. Beehives, frames and other wooden parts after thorough cleaning are disinfected with the fire of the blowtorch until lightly rusted. Dressing gowns and other fabrics are boiled for at least 30 minutes in a 2% solution of carbonic soda.
Empty honeycomb and with the affected brood, they re-heat the honeycomb into wax, and burnt the mervel. Honey from the honeycomb of sick families is pumped out and stored in a sealed container. Implement it in the fall or winter only for food purposes. To use such honey for feeding bees it is impossible, as it will cause new infection of families.
Medobonku and small metal inventory after washing with hot water is disinfected with 2-3% liquor solution and again washed with water; drainage water is poured into a tightly closed pit of at least 0.5 m deep. The parking places of the hives are burned with the lamp’s flame and dumped with a shovel.
American foulbrood
