During the growth of bee colonies, swarms are formed and formed. Despite counter-measures, swarms often fly out of hives, are planted on a tree, shrub or specially arranged near the apiary, and after a while fly away to a new place. The loss of a swarm results in a shortage of a certain amount of honey and honeycombs. To prevent the release of the swarm in the absence of the beekeeper, homemade roo-catchers of different designs, special devices, and appliances are used.
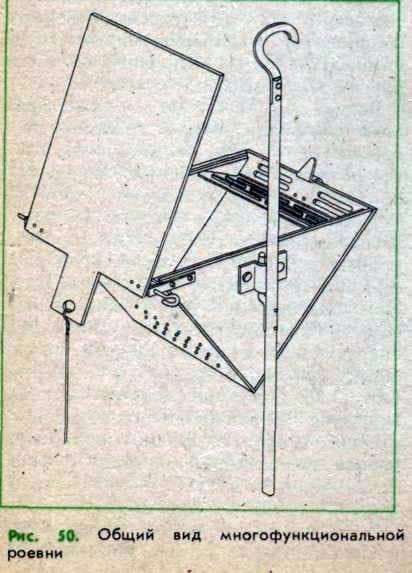
A multifunctional project, the general view of which is shown in Fig. 50, one allows you to combine several operations: removing the swarm, storing it in a cool room, transplanting bees from the rovney into the hive, selecting the uterus from the swarm, catching the drones, detaining the family in the hive of the uterus, baiting and catching swarms, etc. To perform all These operations usually require three or four devices. In addition, the application of this method allows minimizing the trauma or loss of bees and uterus.
The flat is a V-shaped box of a prismatic shape, the open facet of which has dimensions equal to the dimensions of the hull of the multi-hull hive in the horizontal plane, they are closed with a lid hinged on the hull with a possibility of extension along its ledges.
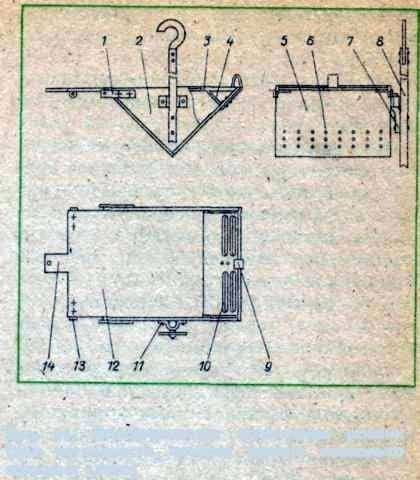
Fig. 51. The constructive design of the rovnya (for clarity, the cover of the rovnya is somewhat shifted to the left)
The corpus corpus is shot down from two lateral planks 2 having the shape of an isosceles rectangular triangle and two rectangular walls 5. Round holes 6 of small diameter are drilled in one of the walls for ventilation of the rova and fumigation of the bees. On the opposite wall, elongated holes 10 are cut, necessary for the passage of bees into the roe, remaining outside after closing the lid, and the latch 9 is fixed. On the outside, the apertures 10 are closed by flaps (not shown in the figure). In the side boards are cut the ledges 3 under the cover, the slots 4 for the installation of the dividing grid, fixed the two brackets 1. The plywood lid 12 with the handle 14 and the brackets 13 is mounted on the hinges to the rivet with a removable spoke axis (see figure 50) passing through brackets 1 and 13. The lid handle has, at the end, a hole for fastening the rope or line. With the help of the bracket 11 and the pin 7, the hook is fixed to the pole 8. The separation grid, shown in Fig. 52.
A multifunctional workstation works as follows. In the case when it is necessary to remove a highly swarmed swarm, the rover is put on the pole pin and raised to the club in the position shown in Fig. 50. While holding the lid in the open position with a rope, the pole is hooked by the branch of the tree, where the swarm is planted, and the bees are shaken off into the rover. After shaking, the rope is loosened, while the lid under its own weight drops, bends the elastic latch and is firmly fixed by it in the closed position. Some time after this, the roevna is left in place / the swarms of the swarm so that remaining bees gather through holes 10. Having lowered the roevna, it is removed from the pole and put in a dark cool place. In the evening, when the years of bees begin to abate or completely cease, The rovnyu with the bees is carried to the apiary and placed with a lid down on the hive previously prepared for the swarm, with the lid removed. From the brackets, the axle (spoke) is pulled out and the lid is opened by the handle, sliding it in the ledges. Bees quickly move to the framework of the hive.
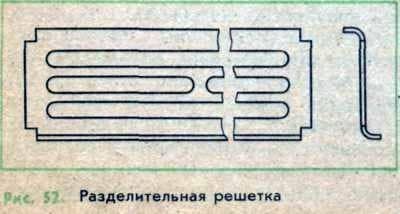
If only bees need to be removed from the rove, leaving the uterus in it, then before the removal of the swarm into the grooves 4 an additional grating is placed (see Figure 52), and when the swarm is transplanted into the hive, the lid is only shifted to the edge of this lattice. In the holes 6 of the song, smoke is emitted, and the bees pass through the grill into the hive. The uterus can not pass through the bars and remains in the village, where it is taken and used for its intended purpose.
In swarm time, if the beekeeper needs to absent himself for a while. from the apiary, remove the lid of the hive of the swarm family, and in its place put the rovnyu with the lid extended and the open bolts on the holes 10; in the hive all the tapes are closed. If, in the absence of the beekeeper, the bee family releases the swarm, the uterus can not pass through the holes 4, and the swarm will return to the hive.
When catching and transplanting into the hive swarm in order to reduce the labor costs and time immediately after its departure, the multi-hull hive of the detached family is transported by a lift truck to the side, and in its place is put a single-hull with a prepared nest and the top with a detained uterus. The swarms of the swarm will gather in the hive hull, installed on the site of the maternal family, from where they can easily be transported to the permanent place assigned to them in the apiary. After flying over the bees, the uterus is let out, the urchus is removed, and the hull is covered with a beehive lid. The family that released the swarm is returned to their original place.
Since both the uterus and the drones can not pass through the dividing grid of the rova, it is possible to use the rovney to prevent pairing of queens with related drones, as well as to catch both of them in necessary cases.
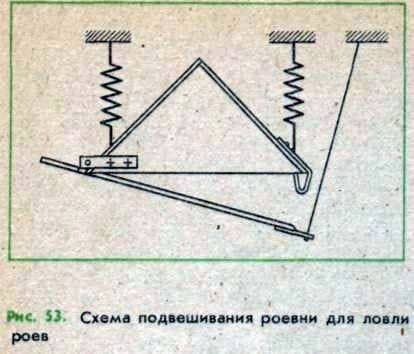
Roevnia can also serve as a sword for catching swarms. In this case, honeycomb is attached to the honeycomb. Further, the roving is suspended on springs to the tree branch, as shown in Fig. 53. The rope’s lid is connected with the branch of the tree so that the lid is ajar and forms a kind of flying board with a slit-fly. When flying a swarm, the flat under its weight moves down to the lid, and at a certain moment the latch acts, fixing the lid in the closed state. The bees that remain outside after closing the lid go into the syringe through the holes. In this situation, the rova provides normal livelihoods of bees before the arrival of the beekeeper.
With the help of a multifunctional roevny it is quite easy to form a crucible nucleus for pairing queens and other purposes. During the flight of young bees, a multi-hull beehive is lifted from the stand by a lift truck and set aside, and in its place a pallet is put and equipped with honeycombsrovnju with the shifted cover. To the bees, going into the chickens, passed only to the sow, the space between the pallets and the lid of the quill must be covered with a liner. Returning from the flight, the bees go into the rover. After they are basically gathered, the lid is pushed, and the roving with the young bees is taken to a cool dark room, and the hive is returned to its place. After two days in the evening, the body of a multi-hull beehive is framed with honey or sugar syrup, placed on the bottom of the hive, and then on the stand. Observing precautionary measures, they plant a barren uterus. On the body put a rovnyu with bees, push its lid to the bees crossed the frame. The liberated burrow is removed, and the hull is covered with a beehive lid. The bees selected in this way without disturbing the nest are well received by the uterus.
The described rovnyu can be successfully used in most operations on the apiary, not only with multi-hull beehives, but also with hive-lounges, if not covered by the framework, sheet, plywood or cardboard.
Рамки для маточником. Крепление для ульев.
Fixtures and fixtures