
Tell the growers about the importance of bees in the pollination of fruit-berry plants is not necessary, because everyone knows: the more they visit flowers, the higher the harvest.
Honey bees perform about 80% of pollination in the gardens, and the remainder are wild single bees, bumblebees, other insects.
In recent years, the number of bee colonies in the population has decreased through illnesses (especially varroatosis, etc.). In addition, most of the wintering families are weak and perform 2-3 times less work in spring than the strong ones. Hence – under-pollination, a decline in the yield of gardens.
In collective and private gardens, a wild single bee of red osmium, specialized in pollination of fruit and berry crops, is successfully used at the Poltava Agricultural Research Station. For almost two decades a small initial population of a hundred individuals collected in the outskirts of Poltava has been increased to 5 million. Such an apiary of bees provides pollination of 1500 hectares of gardens. In the last five years, the station has sold over 3 million cocoons more than five hundred customers.
Osmium has a number of valuable qualities and as a pollinator. It does not compete with the honey bee of the food source, since collects mainly pollen and honey – the nectar celebrated simplicity retention, exceptional peaceful, does not need to fertilize the sugar syrup, protein feeds and works on cloudy cool days when honey bees are reluctant to fly from the hive.
Biology of osmium is largely different from the biology of honey bees. They live not by families, but by colonies, without biological integrity. Working bees are females. The role of males in pollination of flowers is insignificant. Males live to 20, and females live up to 45 days. Flight-pollinating activity of the population lasts 40-45 days. In the Forest-Steppe of Ukraine, red osmium works from the third decade of April until the end of May – beginning of June, pollinating apricots, peaches, cherries, cherries, plums, pears, apple-trees, currants, gooseberries, strawberries, raspberries, grapes.
Especially good work and propagate midge, when the flowering of some crops varies by others and there is a constant food base and moist soil near the nesting – building material for the fires. Under favorable conditions, the female pollinates up to 100,000 flowers per flight season.
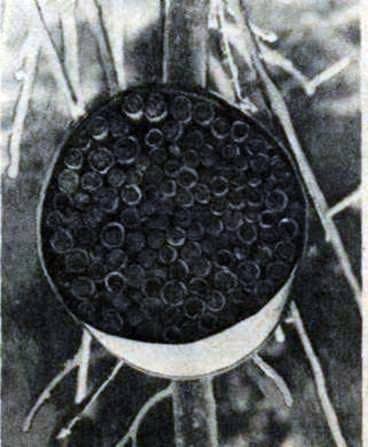
Hive for wild single bees (nest tube, populated by osmium).
In the after-flight period, osmoses are in the intermediate stages of development, reaching the adult state in the autumn, but at the present time the bees do not leave the cocoons, but fall into diapause. In winter, cocoons are kept in unheated rooms at temperatures from +2 to -25 њ C. Such a temperature fluctuation negatively affects the bees.
In the spring, when the temperature of +2 …- 3 њ у is set in the storage facility, the cocoons are transferred to the refrigerator and stored under the freezer at the same temperature. For 4-5 days to the beginning of flowering of early honey-plants (white willow, common hazel, common maple, apricot, etc.) in the gardens exhibit uterine hives in which cocoons are placed, and workers – for nesting bees.
Uterine hive is a box of simple construction, protected from sunlight and precipitation, into which pods are poured by 3-4 cm thick.
Working hive – a metal or wooden box, which is tightly stuffed with reed pipes length of 150-200 mm and a cavity diameter of 7-10 mm. Hives are suspended under the roofs of buildings or in specially equipped shelters.
The males’ single exit from the cocoons happens even on the day the bees are carried to the garden, if the air temperature rises to 8-10 њ C. With further warming, there is a massive output of males, and in 1-3 days – and females. At 11-12 њ C or higher, males begin to carry out mating flights around the hives.
Mating takes place directly near the nests: on the roof of buildings, on the ground, etc. In this case, a significant number of insects can be destroyed by passers-by and transport. Therefore, the hives should be placed no closer than 5-10 m from the roadway. Two days after mating, females begin to build nesting rooms and collect pollen.
For a five-time visit to the flowers of an apple tree, it is enough to have 1.5-2 thousand females per hectare, for which it is necessary to put 4-5 thousand cocoons.
Positive results of application of red osmium in greenhouses and greenhouses as pollinators of cucumbers, tomato, other vegetable and melon crops have been received.
Если у пчел вши. Зимовка пчел в павильоне.
Breeds of bees