
When cleaning the hive, brown spots are especially carefully scraped – traces of diarrhea during wintering. These spots can serve as a source of spores of a dangerous disease of adult bees – nosematosis. Carefully cleared of scum, dirt and stains of diarrhea, the hive and plaited boards are burned with the fire of the blowtorch until the walls are lightly heated. At the same time, it is ensured that the flames and the pilot holes are treated both inside and outside.
After preparing the hive, they begin to transplant the family. The beehive with the bees is removed from the pegs and placed on the side or back from the former place on a previously laid on the ground empty store or a special stand. On the pegs put an empty disinfected hive. From the nest one by one takes out all the frames one by one, shakes the bees from them into a clean hive and quickly cleans the wooden parts of the frames, removing propolis, wax, traces of diarrhea and mold. The cleaning of the frames is carried out immediately near the hive above the box or above the old nest. When rearranging the frames, the net hive is especially cautious with the honeycombs filled with the brood.
They should not be kept outside the nest, so as not to catch larvae and pupae. Bees from these frames should not be shaken either. When completing the nest in a new hive, observe the previous order of the frames. If the apiary is unsuccessful for nosematosis, the honeycomb with traces of diarrhea and not containing brood is removed for subsequent disinfection and replaced with clean or pre-disinfected. On honeycombs with brood, the cleaned bars of the frames are wiped with fleece soaked in a 4% formalin solution. These frames are also put in a new nest, but they make conditional marks on the bars that they should be removed in the summer for complete disinfection or culling. The frames in the new hive are covered with a clean canvas.
Disinfection of the canvas is carried out in advance by boiling in water for 10 … 15 minutes. To relocate the non-flying bees that remain on the walls and the bottom, the old hive is brought to the front wall of the new hive and slanted so that the incoming board of one hive is slightly located on the board of the other. Then the smoke is expelled by the remaining bees from the old beehive to the new one.
Sometimes, during a transplantation, the uterus, which happened to be accidentally on the wall of the hive, together with a handful of bees, is puffed into the depression near the two-walled beacon inserts and unnoticed in time by the flame of the blowtorch. To avoid this, it is necessary to carefully monitor the uterus when rearranging the frames and, having found it, put this frame carefully in a new hive. After the transplantation, families from the old hive are removed and attached to a new one. The nest is well insulated and reduces the flow according to the strength of the family. Then proceed to cleaning and disinfection of the beehive released from the bees.
Disinfection of honeycombs and frames. Collect the honeycombs to be disinfected. The bars of the frames are carefully cleaned with a knife and placed in empty hives or dense boxes. The passenger holes in the hives and all the slots are previously well impregnated with clay or putty. Then the frames are covered with an unfilled canvas.
On the canvas put a layer of cotton or rags 2 cm thick, which is impregnated with 80% acetic acid solution at the rate of 200 ml for 12 … 14 nest frames. On top put a well-fitted sheet of plywood, after which the hive or box is tightly closed with a lid. The exposure depends on the air temperature. So, at a temperature above 16 њ C, disinfection lasts 3 days, below 16 њ C – 5 days.. In connection with this, it is better to conduct disinfection in a warm room.
Having set the necessary number of frames for disinfection, cut out the sushi from the rejected frames. At the same time, the first grade (light or light brown) is immediately put on the baking sheet of the solar wax for re-heating. From the frames freed from the honeycombs, the remains of the wire are removed, carefully scraped with a chisel or knife and disinfected with the lamp of a blowtorch.
Carry out anti-inflammatory measures. If the apiary is unsuccessful in varroa-toza (see the identification table on page 158), during the spring period, bees and a number of health-improving zootechnical measures are carried out.
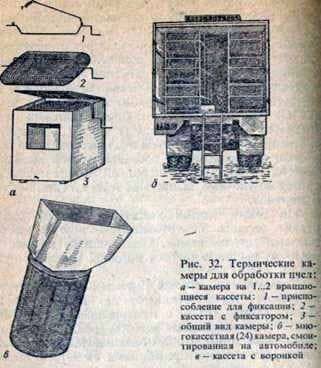
Heat treatment of bees. It is based on the exit of ticks from under the belly segments of the bee at an air temperature above 40 њ C and loss of ability to retain on the host’s body at 46 њ C and above. Work is carried out by one of the links of students under the guidance of a beekeeper in the evening, so as not to cause bee theft. On the eve, bee colonies are prepared for processing, isolating the uterus in a box fixed on the middle part of the frame in the center of the nest and concentrating the nest in the middle of the hive. For this purpose, the frames are moved from the walls to the center of the hive and are protected from both sides by diaphragms.
The bees are shaken from the frame of the treated family through a funnel into a cassette made of metal mesh with cells 2.5 x 2.5 or 3 x 2 mm. The cassette with the bees is placed in a thermal chamber with a temperature of 46 … 48 њ C and is kept in this carefully controlled mode for 12 … 15 minutes, not allowing bees to form tangles. The uterus in the cell for the treatment period is placed in a warm (20 њ C) place. The cassette with the processed bees is brought to the hive, left for 3 … 5 minutes, until the bees calm down. Then, the bees are poured onto the honeycomb frame, after putting an empty magazine or body, and cover with a pillow. When the bees will be placed along the streets, they release the uterus and the nest is put in order.
On the place of the taken cassette in the chamber immediately put in advance prepared another cassette with bees of other family. Scattered mites are selected from the retractable tray of the chamber and destroyed.
Due to the fact that mite females penetrate and lay eggs in drones, bee cells and queen cells before sealing them, before the heat treatment of the family they remove frames with brood and concentrate it in separate families without queens. After 3 weeks, when all the bees come out of the cells, these families also heat and strengthen other families. If the brood is small, it is destroyed.
Installation and inspection of mesh subframes.
In dysfunctional varroatoza families, after a spring audit at the bottom of the hive at a distance of not less than 3 … 5 cm from the tap, a mesh subframe with a layer of petrolatum applied to it to collect the mites is placed on it and periodically it is inspected. Upon examination, the subframe is taken out, the metal mesh is lifted, the mites are peeled off the bottom of the baking sheet, a new layer of petroleum jelly is put on it and placed in a hive. In doing so, pay attention to ensure that the mesh was well fixed in the frame of the stretcher and did not touch the baking tray.
Use of frames with drone cells. The varroa mite breeds more intensively in the drone brood. To concentrate the parasite in the nests of disadvantaged families near the brood, put a frame with drone cells or a drone wax as a bait for ticks. After sealing the larvae, the frame is removed, the cells are carefully printed first with one, then on the other hand, the pupae are shaken out of the cells together with the mites and destroyed, and if necessary, washed with a jet of 2 … 3% acetic acid solution or hydrogen peroxide. Such a framework is better to have at least 3 per family.
First put one frame from the edge of the nest, a week later – the second frame from the other side. After 2 weeks, the first frame is replaced with a third one, etc. In multi-hull beehives, a combined frame is used, for which a frame with a bee sting or honeycomb is attached to the frame with a honeycomb or honeycomb from below.
Installation of troughs. On all hives, the apiaries of the unsuccessful zone in the varroa tosis are set up in the spring with tumblers. The captured drones are burned. Trutnolovki removed during the main bribe. Methods of carrying out the spring audit of the apiary. Usually the spring inspection of the apiary is carried out by a special commission in the first days after the exhibition of bees in warm weather (at a temperature of air in the shade not lower than 14 њ C). This work must be done quickly in order to have time to inspect all the families of the apiary for 1 … 2 days and at the same time not to brood the brood and not to cause bee theft (during the audit period there are often no bribes). Therefore, it is better to familiarize yourself with the technique of carrying out the spring audit of the apiary in a more favorable late spring period, when stable warm weather and the presence of a bribe in nature allow a relatively long time to examine the bee family.
Thus, between the time of the first half of this work – cleaning and disinfection of nests and familiarization with the technique of carrying out the spring audit of the apiary can be a break in a few days or even 2 … 3 weeks. If the weather is warm enough, then both events are held in parallel.
To determine the strength of the family, raise the canvas and count the number of streets well filled with bees from above. However, in some cases, bees can be placed only in the upper part of the honeycomb. Therefore, in order not to overstate the strength of the family during further examination, such a framework is summarized together and at the end of the survey they record the adjusted strength of the family according to the number of frames densely occupied by the bees.
Honey reserves are determined approximately by the area of the honeycomb, which is occupied mainly with printed honey.
So, a full, on both sides sealed standard nest frame accommodates 3.5 … 4 kg of honey. If honey occupies only half the height of the frame, it will be about 2 kg. A strip of honey in the upper part of the frame with a width of 7 … 8.cm contains up to 1 kg of honey, and a strip with a width of 4 cm – 0.5 kg. The amount of honey will be less than the specified amount if the part of the sealed section of the honeycomb is occupied by a pearl (which can be easily detected if the frame looks at the light) or the thickness of the sealed bar is too small (less than 30 mm). On the other hand, the amount of honey should be increased if, in addition to printing, there is also unsealed honey in the lower or lateral parts of the frame. To check the eye estimate of the amount of honey, shake the bees from one or two of the outer frames and weigh these frames on a cup scale or, even better, on a spring stalk. In parallel, we weigh a few frames of the land about the same color as the frames taken from the nest. Subtracting the average weight of the empty honeycomb, determine the actual stocks of honey within the framework taken from the hive.
The presence of the brood in the nest is characterized by two factors: the number of frames on which there is brood, and the absolute number of brood (in terms of one frame) found in the family as a whole. Carefully examining the frame outside the frame and discovering the brood, determine which square of the honeycomb it occupies. This takes into account both printed and open brood. The area of the frame, occupied on both sides by the brood, is more convenient to express with a decimal fraction. For example, the brood occupies 0.1, 0.2, 0.3, etc., parts of the honeycomb. The beekeeper, who conducts the registration, records in one column the amount of honey (in frames) in the nest, in the other – the amount of brood on each frame.
When inspecting the brood, attention is also paid to the quality of the brood.
In a prosperous family with a good uterus, larvae and pupae occupy most of the honeycomb in a row, without omissions, and among them there is no horny brood brood. Especially carefully examine adult unsealed larvae. If among them at least single sick or dead larvae of yellow, coffee or dark brown color are found, then the family is sick with a dangerous disease (most often European foulbrood). This is immediately reported to the teacher and the beekeeper and, at their request, they prepare samples for sending to the veterinary and bacteriological laboratory to clarify the diagnosis. In this case, out of the frames of sick families, cut pieces of honeycombs measuring 10×15 cm with dead larvae and pupae. Samples of honeycombs, without wrapping paper, are placed in a wooden box, separating the honeycombs of the honeycomb from the bottom and the cover with wooden slats.
In case of single cases of detection of diseases, further examination of families is carried out with observance of quarantine rules: wash hands with soap after inspection of each sick family, water after washing is poured into the pit and covered with earth, chisels lightly burned with blowtorch lamp,
When revising a strong family with a large number of compact and healthy brood, it is not necessary to search for the uterus. Verify its presence can be due to the presence of eggs in the cells of honeycombs.
At the end of the family survey, the obtained indicators summarize and add to the list of the spring audit of the apiary.
Expansion of nests. This operation can be performed in parallel with familiarizing the students with the technique of carrying out the spring audit. The nest needs to be expanded only if the space between the plank and the edge frame is occupied by the bees or if the brood is already on the second frame from the edge. For the spring expansion of the nests in advance prepare well-built light-colored honeycomb with bee cells, in which 3 … 4 generations of bees have already been bred. The honeycomb is placed between the extreme aft frame and the last frame with the brood. If the family is already strong and by the time of inspection has 5 … 6 complete flow limits, then to expand the nest, you can immediately put two honeycombs, placing them on the edges of the frames with brood.
When there is at least a small bribe (100 … 200 grams of nectar per family per day) in nature, to expand the nest, frames are framed with artificial wax. A peculiar signal for setting up an artificial wax is whitewashing the honeycomb with a new white wax, which the bees build on the edges of the cells in the upper part of the frames.
Frames with an artificial wax are also first placed at the edges of the brood (wire to the center of the nest). At subsequent inspections of the family, the framed frames are rearranged to the center of the nest, and new frames with an artificial wax are put in their place. If the family is strong, then at the onset of a stable warm weather frameworks with an artificial wax put immediately at the center of the nest.
When the wax is used, the nest is updated more quickly, in the freshly built honeycombs, 2 … 3 generations of larvae will be hatched by autumn and these honeycombs will be suitable for wintering bees. It is undesirable to put waxed frames next to the honeycombs, which are strongly thickened at the top. In this case, the cells of the upper part of the new cell will be very small.
Addition of bees with medicinal syrup. If on the apiary families that are sick with European foulbrood (detection of diseases of bees by external signs) are found out, the beekeeper after the specification of the diagnosis in the veterinary-bacteriological laboratory proceeds to treatment.
The nests of newly infected families are cut and warmed well. The bees are given a medicinal syrup. To do this, add one of the medicines to the sugar syrup (1 part of sugar and 2 parts of water), cooled to 30 њ C. For 1 liter of syrup, biomycin or streptomycin is taken 500,000 units, neomycin, erythromycin, oxytetracycline or tetracycline at 400,000 units, methicillin 350,000 units, norsulfazole sodium 1 g, sulfantrolium 2 g.
The finished medicinal syrup is given to sick families at the end of the day at the rate of 100 … 150 ml per 1 street. It is poured into metal feeders or glass jars that are put over the middle of the nest. The open part of the nest is covered with a plate or a second canvas, and a pillow is placed over the feeder and the hive is closed with a lid. Summer reduces, preventing theft of bees. The dessert of the medicinal syrup is repeated every 5 … 7 days until complete recovery, and the conditionally healthy families are given a therapeutic syrup 1 … 2 times for prophylaxis.
Содержание пчел на платформах. Инструкция по применению щавелевой кислоты.
Contents and breeding of bees