
Not so long ago, hives of various designs were used in our country. Each experienced beekeeper considered it necessary to invent his hive design, often without taking into account the biological and physiological needs of the bee family.
The variety of hives caused a lot of inconvenience in the care of bees, made it difficult to standardize the size of the honeycomb leaf, the size of the honey extractor,
The modern standard beehive should provide the best development of the family, be comfortable in work, easy, simple in the device and cheap.
Hives are made of dry wood of soft breeds: pine, spruce, linden, fir, cedar, aspen.
To lengthen the life and give the beehive a beautiful appearance, it is first olifed, then shpaklyuyut and painted in the colors recognized by bees – mainly in yellow and blue, preferring light shades, less warmed in the open by the sun. To color the hives, you can use “silver”, the color of which the bees take for blue-yellow. It is noticed that hives, painted in light colors, for bees outside the greenhouses will be cold, since they reflect the sun’s rays. To avoid this, hives, painted with light-colored paint, are wrapped in a spring or autumn with a ruberoid or pergamon, the dark color of which, absorbing the sun’s rays, warms the beehive and the bee nest. It should be noted that in new and in freshly painted hives, bees hibernate worse than in unpainted and old ones.
The existing hives in the device are extremely simple. They consist of a box that is a four-walled box, in the upper part of which are chosen folds for hanging the frames, the magazine extension or the hull, the bottom, the overburden and the lid.
Standard beehives for design are of two types: risers and deck chairs. When determining the size of the framework, it was assumed that bees are better in hibernating in high-hive beehives, and a low frame is more acceptable for the development of bees in spring. But as in the hives it is possible to use a frame of only one size, then the outer length of the frame of all designs was made to the same size – 435 mm, they differ only in height.
Hive stands have a hull for 12-14 frames 300 mm high (Dodan frame), such risers satisfied bees both in wintering and during spring development. For each riser can be supplied: another body with a conventional frame or 1-2-store extension with a frame height of 145 mm.
The store extensions of the 12-frame hive, placed one on top of the other, are equal in size to the body, which makes it possible to use a nest frame or two sets of half-frames if necessary.
To a lesser extent, multi-hull beehives consisting of 3-5 frames per 10 frames, whose height is 3/4 of the height of the conventional frame (230 mm), are less common.
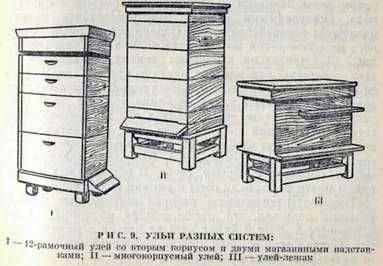
Sun beds accommodate from 16 to 24 standard frames, sometimes they are put on the store extensions.
Until recently, it was believed that double-walled beehives would be warmer for the bees in the cold, and warmer in the greenhouses. Practice has shown that, regardless of whether the hive has double walls or not, the temperature in the hive in winter will be approximately equal to the outside. In the central regions of the country in single-walled beehives heated by the sun, bees develop in greenhouses and free will not worse than in double-walled bees.
In the 40-50’s. in hothouse farms, glazed beehives were widely used. In the middle of the front wall of the hive, approximately half the area was made glazed. In cold weather, to reduce heat loss, the glazing was covered with a pad.
It was believed that the glazed hive is more suitable for the development of the family and the work of bees in greenhouse conditions. It was tempting to learn that in a glassed hive the temperature of the nest is better maintained, its fluctuations are reduced, the development of bees from the egg stage to the adult insect is accelerated by 1-3 days, the dampness is eliminated, the egg laying period for eggs is increased by 2 weeks in autumn and the masonry is accelerated in the spring, honey consumption decreases with older bees, bees are less prone to disease and many times more honey is collected.
Many beekeepers of European countries became interested in clarified beehives. However, soon after their widespread use, many beekeepers were disappointed in them. Indeed, in strong families, irrespective of whether they are clarified or not, the bee brood develops faster than in middle and weak families. It turned out that the bees in the glazed hives, especially the young ones, found it difficult to find a vent hole, as they were provoked by the light coming through the glass, which made the bees more angry. In strong illumination, the temperature in the nest increased. This often led to the death of the brood and the breaking of the honeycombs. In the glassed hives, the bees almost did not build honeycombs and changed the queens more often.
Beekeepers – hothouses, introducing glazed beehives into greenhouses, believed that bees crawling along the glass of the hive would get used to it and less fight against the roof of the greenhouses. However, the glazed hive, when widely tested, did not confirm its advantages.
Which of the existing hives is better and most suitable in greenhouses?
The choice of the hive of the appropriate design determines the zone of its application, the habit and skill in working with bees.
An important detail of the hive is the frame. They should be without distortions and have exact dimensions, the side strips should not bend when pulling the wire, the distance between the walls of the hive and the side slats of the frames should be within 7-8 mm. At a greater distance, bees build up free space with honeycombs, and at a smaller distance, they glue the frames to the walls of the hive. Both make it difficult to inspect the nest.
The inconvenience in working with bees creates a frame with delimiters. The dividers represent a slight widening of the lateral bars in the upper part, creating the stability of the frames when transporting bee families on a bad road.
In a hive completely filled with delimited frames, it is impossible to press them so that, without hampering the bees, one of the first frames can be extracted. The dividers are pre-polished, and when the frames are separated, jerks are created that irritate the bees. When inspecting part of the nest, you can not move the frame to its original location, so as not to suppress bees and especially the uterus. It is not possible to regulate the width of the streets, and this in greenhouse farms have to do. When the honey is pumped out on chordial honeycombs, the separators interfere with the tight fit of the honeycombs to the cassettes, which causes them to break. In order not to pressure the bees, each frame is raised from the hive and lowered. It takes time and labor.
If the bee family is not examined for several days, the frames are so stably attached to the folds of the hive that it is difficult to move the chisel from the place and no dividers are needed during transportation. In extreme cases, across the frame, on the shoulders, nailed 2 racks.
Beekeepers of many hothouse and commodity apiaries in their practice, the dividers on the framework are constructed.
For fencing in a hive unoccupied by bees, a plaque (diaphragm) with a thickness of 10-15 mm is used. The diaphragm, like the frame, is supported by the shoulders on the folds of the inner walls of the hive. In length, it corresponds to the internal dimensions of the hull, and along the height at the bottom of the hive forms a gap for the passage of the bees.
For the upper shelter of the nest of bees, we use canvases or ceiling plates with a width of 7-8 cm and a thickness of 1-1.5 cm.
The underlay flooring from the ceiling boards is above the frames at a distance of 1 cm. Due to the over-frame space formed by the bees, it is more difficult for bees to maintain the necessary heat-air mode in the brood portion of the nest.
The advantage of the canvas in front of the ceiling boards is that it lies directly on the frame, creating a certain microclimate in each street, which is especially important in the northern and central regions.
In greenhouses where there is a relatively high temperature, wax moth larvae find shelter between the canvas and the frames, which inflict great harm to bees, unless regular inspections of bees are carried out and larvae of moths are not destroyed.
With the emergence of a framework hive between beekeepers there is a dispute, what is better for hiding a nest – lobes or ceiling plates? For the spring development of the bee family, the canvas is better, but in the summer, the hive will have less overheating at the ceiling shelter of the nest. Therefore, when choosing a ceiling shelter take into account the climatic conditions of the terrain and the possibilities of the economy. So, in the south of the country, canvases are less desirable, since they impede the ventilation of the nest and contribute to the development of moths.
In the original practice of greenhouse keeping of bees in the summer we applied canvases to ceiling boards, but the benefits from this event were not found and gradually began to use only the canvas to facilitate the inspection of the bee families.
Applying canvas, you must reckon with the instinct of bees. In the hollows and other dwellings of the bee, before removing the honeycomb, remove all the rotten ones from above, and then they begin to rebuild the honeycombs and propolize the top to eliminate the further decay of the wood. So the bees act in the hives; if an old, rare sacking is used for the above-frame shelter, then the bees gnaw it. Dense canvas serves bees for decades. It is of interest to use a ceiling shelter for frames used in the subsidiary farm.
During the wintering of bees, he, like many beekeepers, puts unpolished sacking on top of the frame, and uses a film for the time of the spring-summer-autumn period. They noticed that with an impenetrable film ceiling shelter in the nests of weak bee colonies, condensation of moisture forms, and medium and strong bee colonies do not. The beekeeper believes that with the film shelter the frames of the bee largely use the water condensate and in the inclement weather, which is not flying for bees, less experience in it needs. The film allows you to see the density of bees sitting around the nest without opening the nest. To the above, we should add that the upper bars of the frames under the film are propolized less.
Щавелевая кислота инструкция. Пчелы пьют воду.
Hothouse beekeeping