
In the system of measures to increase the waxy products of the apiary, timely nest change is very important. This method is widely used by many beekeepers.
However, the timely replacement of nests, being the most important and necessary measure, is not the main source of obtaining a large amount of wax and a in the apiary.
The basic methods of increasing the wax productivity of bee colonies are the application of the wax-building framework. Usually they are called building frames.
Building framework. The main importance of the building framework is that only with a wide and correct application of them you can get the most amount of wax, and moreover – the highest quality. Apiaries, which do not use building frames, that is, do not give a place in the nests or near them to build combs with bees, often have low wax productivity, even in conditions of a good fodder base.
But the significance of the building framework is not limited to this.
Bee families, in which the building framework is applied, are distracted from swarming, as their bees are heavily loaded with work on waxwork. Such families for a longer period, and sometimes all; the season is in working order; build up more strength, better use bribes and give more honey.
When using the building frames, the quality of the sockets of the socket improves. This happens for the following reasons. In natural conditions, each developing family at a certain point begins to prepare for swarming and at the same time builds up the drone honeycombs to remove the drones needed during the pairing of young queens.
It should be pointed out that the construction of the tartar honeycombs and the withdrawal of the tartar brood is one of the links of the strongest instinct – reproduction. Therefore, if there is an empty place in the nest of bees during the pre-erid period, then, in the presence of a bribe, the bees very quickly build it up with drone honeycombs. But if there is not such an empty place, then to satisfy the instinct of detaching the drone honeycomb, bees redo some of the parts of the reconstructed artificial honeycomb, and still build up the drone cells.
In some cases, they convert part of the cells from bees to drone, even on young honeycombs. If the bees are put into the nest in a timely manner, the building frame, then they will build a drone honeycomb in it, without degrading the quality of either the artificial artificial honeycomb or the existing honeycombs. Only by applying the building framework, it is possible to achieve that all honeycomb cells will have exclusively bee cells.
In the same way, the presence of a building frame in the nest of the family satisfies the instinct and the uterus: it lays the drone eggs in the built-up honeycomb of the building frame in the pre-erid period. If the uterus in the pre-erect period is not allowed to lay unfertilized eggs in the drones, then it will partially lay them in the bee cells, much less in the honeycombs of the honeycomb. Having sowed a significant area of the tartar honeycomb of the building frame with unfertilized eggs, the uterus will later lay the fertilized eggs normally.
Finally, we note another important importance of the construction framework: its use facilitates the work of the beekeeper and makes it more productive. Applying the building framework, the beekeeper can only on the basis of their inspection, not dismantling the whole nest, determine the state of the bee family at the moment. If, for example, a certain part of the built-up sections of the honeycomb of the building framework (“languages”) has bee cells, then the family is in good working order.
The working condition of the family is also evidenced by the speed of construction of the honeycomb of the building frame and the complete lack of bells on it. But if, in the presence of a bribe, the construction of honeycombs of the building frame is slow and there are bowls on its honeycombs, this indicates the approach of the family to the swarm state.
Our observations prove that if the building frame is in the brood portion of the nest, the first swarm queen cells in most cases will be on it: here are the most convenient places for building queen cells, and bees are easier to build than on the old honeycomb. In addition, according to the presence of the injection (liquid honey) in the honeycomb of the building framework and the intensity of detuning the family in comparison with other families, one can judge the use of a bribe by the family, its quality, and so on.
Thus, the building framework is also control. Using them, the beekeeper can not waste much time inspecting the nests of families, do not disturb bees in vain and do not interfere with their work: enough, removing the cover and 1-2 ceiling or canvas, raise the frame and literally in 1-2 minutes to learn the most important thing about the development of the bee family at the moment. The better the condition of the apiary, the more bee colonies are stronger, the more important is the control over their condition through periodic inspection of the building frames.
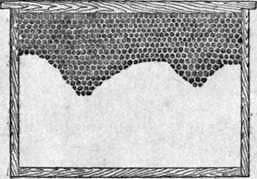
Fig. Building frame with a built-up honeycomb.
Building frames come in different devices. Many beekeepers use the simplest type of building framework. They instead of the cellular frame of the nest put only the top bar from the frame or put empty frames. In both cases, the upper brusod is stuck in a narrow strip of an artificial honeycomb before staging in the hive, so that it is more convenient for the bees to start detuning the honeycomb. The disadvantage of this type of building frame is that a relatively small group of bees is occupied here by the construction of a honeycomb, and a significant part of the building energy of the family is not used.
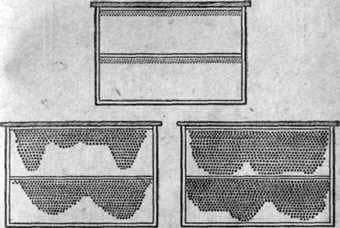
Fig. A building frame with a longitudinal strip separating the clearance of the frame in half: at the top, waxed with narrow strips of a honeycomb; below – the type of building frames for the bees’ detuning.
Much faster is built up honeycomb when the ordinary empty frame is divided by one or two horizontal slats into 2-3 approximately equal parts. In this case, a considerable number of bees can be employed for detuning. Using for this purpose ordinary store half-frames, to which the bars (upper and lower) attach narrow strips of artificial wax, or beginners from young honeycombs of natural constructions (“languages”). With a good feed base, this ensures that more than 1 kg of wax is obtained from each bee family per season. The same is done by other beekeepers.
Some beekeepers even use planks as building frames. Platen boards, used by him, are ordinary empty frames, to which, on one side, plywood sheets are nailed to the entire lumen of the frame. The upper block of the frame is padded with a strip of artificial honeycomb. Sometimes the entire inside of the plywood in this frame is waxed, which makes it possible for bees to start building a honeycomb on plywood in many places.
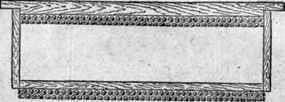
Such a frame is very easy and convenient to inspect, removing only the upper bar along with the honeycomb built on it. When it is used there is no danger of cooling the nest, so it can be used starting from the very first May bribes. Such a framework in a warm time can be put in the center of the nest, and not one by one, but 2-3. In them, honeycombs for use on wax are built in the upper part of the nest where it is warmer so the detachment of the honeycomb on such a framework is more vigorous than with other types of frames.
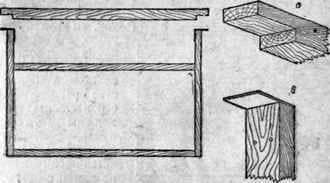
Fig. Building frame with detachable top bar:
A – the end of the upper bar; b – the upper part of the side bar with the iron plate (hanger).
The question of staging the building frames in the nest of bee colonies is very important for production. In beekeeping literature, there are often indications that the construction framework should be set only after a complete detachment of the sockets of the nest on an artificial wax and after the stock of land has been created. But such an installation in practice can often prove harmful.
After all, the change of nests and the detachment of honeycombs into the reserve can, for various reasons, take a lot of time. One of these reasons may be the small wax supply of the apiary, insufficient amount of wax and artificially waxing in the farm. This can only be remedied by the extensive use of building frames, which will enable timely extraction of wax for the exchange of artificial wax.
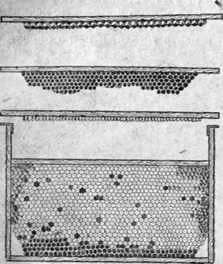
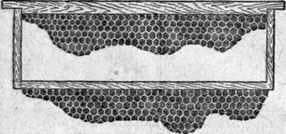
Fig. Detached honeycomb on the building frame: at the top – detachable strip with a strip of artificial wax
In the conditions of Ukraine, the construction framework should be put in families with cash, the first bribes at which honeycomb construction is possible, and have them in the hives all the time, until the end of the last bribe. In the presence of bribes in most regions of Ukraine, the building framework should be in families in May, June, July and August. In May, the frames are mainly framed with a detachable upper bar, and later of other types. The number of building frames in the family: depends on many conditions. The more abundant the bribes, the stronger the family and the greater the need for wax, the more the bees should be loaded with waxwork. In strong families, the building framework can be 2 to 3 at a time.
In most cases, the detachment of the artificial wax and the construction of the building frames should be made simultaneously, placing them on both sides of the brood portion of the nest. It is better to use building frames with detachable upper bar.
It must be strictly monitored that in all periods of the warm part of the spring and summer season, in the presence of a bribe in each bee family, there was a place for bees to build honeycombs used for wax.
Cut out the constructed honeycombs from the building frames with their intensive detuning follows approximately every 3-4 days, so that the bees do not spend too much energy and food on the brood brood brood.
Other methods of obtaining wax. The next important technique, which allows obtaining a significant amount of wax, is the correct work to limit the number of drones in the apiary. Typically, for the removal of drones in the apiary, several highly productive families are distinguished.
In the remaining families the withdrawal of drones is limited. The main measure to limit the withdrawal of drones in families is the use of quality honeycombs and giving bee families an artificial honeycomb within the framework of detuning. However, in almost all normally developing families, in the pre-eriod period there is a certain amount of the tartar brood located mainly on the lower corners of the honeycombs.
In order to prevent the withdrawal of an excessive number of drones, many beekeepers cut off the upper part of the sealed drone brood. After setting such a framework in the nest, bees immediately begin cleaning the tartar cells from the remains of the brood, and the uterus secondarily sows them with unfertilized eggs.
As a result of this “work” of the beekeeper to limit the withdrawal of drones in a given area of the tartar honeycomb, in the course of a month, not more than one generation of the brood brood, and two, that is, the expenditure of food and energy for the bee colonization of the bee brood not only does not decrease, but it increases considerably. In addition, the beekeeper-cut lids of the drone brood.) Have very little wax.
Some beekeepers spray open brood brood with water, after which it is ejected by bees. But this can not be done, since part of the spray can also get to the nearby bee brood. In addition, in some cells with brood, water can not enter such a large amount that the brood was discarded, some of the larvae may remain in the cells, but the smallest droplet of water larvae weaken, Their resistance to disease is significantly reduced than the soil for outbreaks is created brood.
Advanced beekeepers, act differently. They do not cut off the “heads” of the larvae of the printed drone brood, and the sections with such brood located at the edges and corners of the honeycombs are cut out completely. At the same place, in the presence of a bribe, the bees again build drone honeycombs, and the beekeeper, at the next examination of the nest, cuts them again, without waiting for the feeding of the tartar brood.
All these trimming of honeycomb with drone larvae are used to obtain wax. At the end of the day or not later than the next day, the scraps with the larvae are pounded in the dishes (in order to crush the main mass of the larvae), and then digested. In this case, a significant amount of wax is obtained: often during one day of work the beekeeper can receive this wax 0.5-0.7 kg or more.
A good, higher grade wax can be obtained from a bar – wax lids, cut off when printing out honeycombs during pumping honey. You just have to make sure that not a single crumb of this wax is lost.
In beehive families kept in 12-frame hives with shops, when pumping honey, cuts the store frames by 1/3 of their height, thus obtaining 200-250 g of beeswax from the bee family during each pumping of honey. The empty space at the bottom of the honeycombs of the store frames of the bee is very quickly built up with a bribe.
The use of other wax resources is also of great importance. So, some amount of wax is in the litter among the dead bees (in the sub-sea), swept out of the hives during the cleaning of the donjes in the spring, immediately after the exhibition of the bees. Therefore, the scum must be sifted. The existing wax lids along with a part of the litter are sifted, separated from the sump, and then re-heated for wax.
A significant amount of wax is obtained by cleaning the frames during the audits of bee colonies and during the operation of the beekeeper throughout the season. It must be taken as a rule that no matter what kind of work the beekeeper does in the hives, he should always have at hand a small box for the collection of wax raw materials: carved honeycombs of building frames, collection of waxen cuttings, cleaning of outgrowths, cuttings of the brood brood, etc.
Even cut queen cells or deleted bowls should not be thrown anywhere, but should be put in a box for further processing on wax. Daily diligently conducted collection of wax raw materials throughout the season must firmly enter the system of work of each beekeeper.
Осы и хищники. Пересылка пчел.
Beeswax