All about varroatosis

No matter how much information is published about varroatosis, the fight against it, interest in this does not decrease.
Prepared article, which contains the most necessary, priority information about this disease, showing the dynamics of the fight with the pathogen.
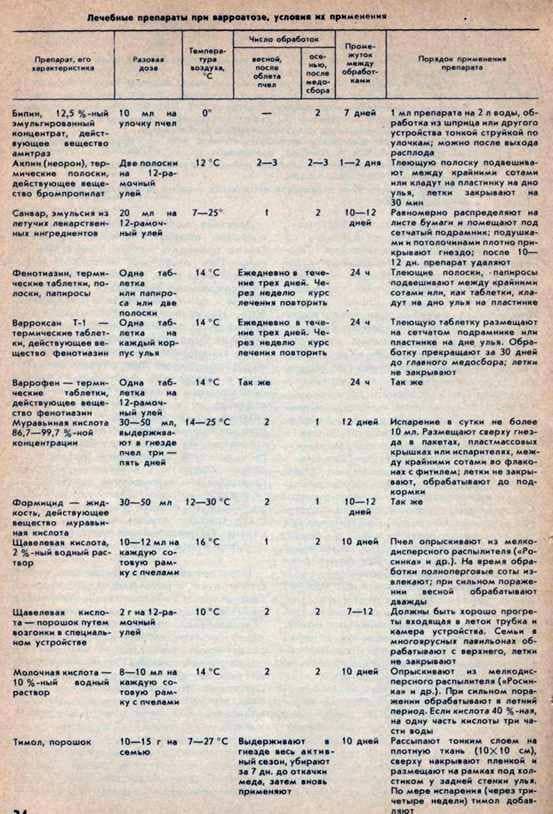
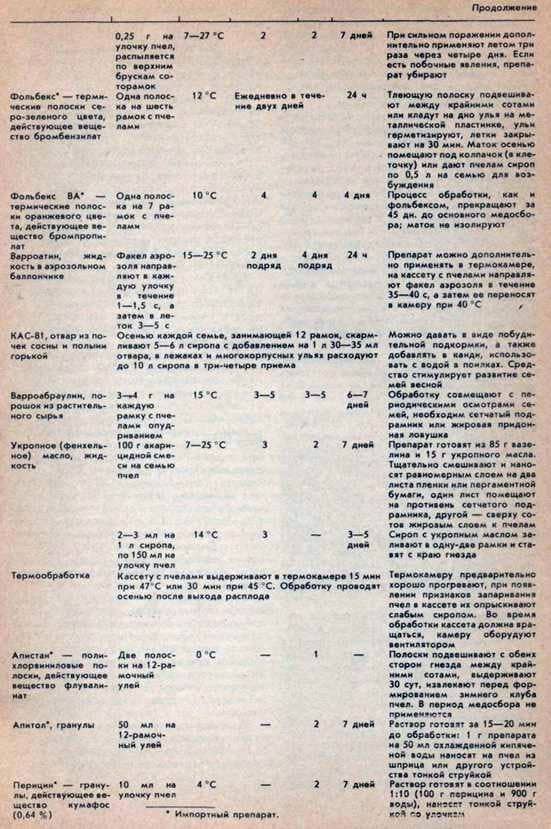
As a result, we offer a kind of “memo” with a unified table of data on medicinal preparations, the timing and methods of their use.
The fight against varroa at the present time is mainly carried out in the following areas.
The first is the use of all possible technological methods:
Removal from the nests and destruction of the affected drone brood (building frames, etc.);
Application of mesh stretchers and fat (powder) bottom traps;
Formation of slack drains;
Use of hive-incubators for growing the affected bee brood;
Limitation of oviposition of the uterus during the period of the main honey collection, etc.
The second is the use of acaricides, which are a powerful factor in reducing the number of parasites in bee families, but are fraught with the “contamination” of beekeeping products and the habit of ticks after repeated treatments. In addition, the effect of many drugs is short-term, and the possibility of use is limited by the temperature of the environment and the biological processes taking place in the family.
The third is the use of thermal chambers of various designs. Processing bees is effective, provides clean production, but it takes a lot of time and a lot of labor.
The fourth is the systemic action on mites with chemical and herbal preparations, when the active substance through the digestive system enters the general cycle of metabolic processes of the bee and mite and kills the latter.
The order of treatments. The most favorable time for chemical treatments is early spring, after a good flight of bees; in the
The action of any drug before the beginning of mass treatment should be preliminarily tested on three families of different strengths. In the absence of negative phenomena – the departure of bees, the discard of the brood, the cessation of the laying of the uterus or its death, etc., proceed to the basic work. At large apiaries, the event must be carried out in a short time, so that the families of the bees are not re-bred.
All chemical preparations should be stored in a sealed container, in a dry, cool and shady room, well ventilated and inaccessible to children, separate from food. Vegetable raw materials are packed in paper or cardboard containers and stored on racks. Each drug should have a label with the name of the drug and the expiration date, with the expiration of which its acaricidal effect decreases. All preparations that are used in the form of solutions or decoctions (herbal remedies) should be prepared before use.
The remaining amount for the subsequent course of treatment is unsuitable.
Precautionary measures. During processing bees strictly observe safety precautions. Work should be in dressing gowns, rubber gloves and respirators. When using drugs in the form of smoke, fumes or fine spraying near the family of bees should be on the leeward side. At the end of the work, wash your hands with soap and rinse your mouth with water. Using thermal preparations, strictly comply with fire protection measures (at the bottom of the beehive smoldering strips, tablets or cigarettes are placed on metal plates or a mesh subframe).
Do not neglect safety when using a thermal chamber: it is installed in a dry room on a rubber mat or wooden cover, preventing moisture from entering the instruments. You need to work together or together to help each other, if necessary. In the apiary, you must have a first aid kit with a set of heart and antiallergic medicines, as well as a means for neutralizing acids with burns (baking soda).
Diagnostics. The effectiveness of antivariate measures depends largely on timely and accurate diagnosis. Every beekeeper should be able to perform it, without waiting for the results of the veterinary laboratory tests. For this purpose, at least 50 live bees are taken from a frame from the center of the nest in a paper bag and shaken out in hot (70 њ C) water in a dish with a white bottom (a cup, a plate, etc.). To accelerate the separation of ticks from bees, 2-3 g of detergent powder is added to the water. The bees are thoroughly washed, stirring in the water. Scattered mites are clearly visible on a white background of the bottom of the dishes. It is necessary to know the degree of mite damage of each family in order to plan the multiplicity of treatments and to predict the outcome of the disease.
According to many researchers, the death of families during wintering occurs when there are more than 20 ticks on 100 bees in autumn, and abundant fertilization of bees with sugar leads to death and with a smaller number (O. Grobov, 1978). In this regard, with a degree of rancidity of 10-20%, urgent measures should be taken to save families. With a degree of bee damage of up to 10%, it is possible to successfully combat invasion. At the present stage, the system of antivariate measures in our country and in other developed beekeeping countries does not provide complete recovery of the apiaries, but only temporarily reduces the number of ticks in the families of bees, but this does not prevent significant reproduction of families and makes it possible to receive marketable products.
Increased resistance of bees. The parasitization of the varroa mite leads to a large loss of protein in the bees’ organism, resulting in a decrease in their life span. Strongly invasive families leave their homes in the autumn or die at the beginning of wintering, if not provided them with timely assistance.
As a protein feeding with insufficient intake of pollen in the hive in early spring or in an unfavorable summer season, bees can be given polyamine. The drug is a balanced mixture of amino acids, of which ten are essential for bees. Produced in vials of 100-400 ml. It is mixed with sugar syrup in equal volumes and given to bees in feeders at a dose of 0.5-1 L and 3-4 times according to the Consumption. During the period of the main honey collection the preparation is not used.
To increase the resistance of families to diseases and stimulate their development, a biologically active substance of plant origin, the biospon, is used.
A complete homogenization for bees is a homogenate obtained from freshly sealed drone broth containing a significant amount of protein. With the help of the building frame, one can remove up to 1 kg of the brood brood from the family at a time, the extracts of which are close to royal jelly in chemical composition.
The homogenate is prepared from the drone brood from bee colonies, which are well-off for infectious diseases, especially for ascosphere and foulbrood. It is used only in its apiaries, without the right to transfer to others. The drone brood removed from the cells is converted into a homogeneous mass on a juicer or meat grinder. If necessary, the preparation of the homogenate for future use is preserved with powdered sugar in a ratio of 1: 2. In this form, he does not lose his qualities for two months if stored in the refrigerator at 0-5 њ C.
If bees are fed a freshly prepared drug, it is added to the sugar syrup at the rate of 1-1.5 kg per 10 liters of syrup in a ratio of 2: 1. For the preparation of feeding take 2-3 kg of canned homogenate and bring with warm water (34-35 њ C) to 10 liters, thoroughly mixing until the sugar powder is completely dissolved. Syrup-like mass is given to bees in feeders or poured into empty honeycombs. The family spends up to 500 g of homogenate.
Antiviral activity should be carried out annually in full. Only under such conditions it is possible to achieve successes in the improvement of apiaries.
All about varroatosis
