
Of course, at home it is difficult to have excellent results when dressing heavy (7-20 kg) skins taken from a cow or a bull, an elk or a wild boar. Therefore, we will confine ourselves to advice on the production of small (up to 2 kg) and medium (up to 6 kg) skins. Immediately warn that dressing skins – an occupation for the patient and needs certain skills, so the robot is advised to start from low-value skins.
Hide the skin immediately after removal. If there is not enough time, it can be preserved. Most often, fresh and dry canning is used and with the help of kitchen salt. In both cases, the skin should be cooled, and it should be degreased. Preservation prevents rotting of the skin, damage to its moth and skin. Dressing skins are conducted, adhering to a sequence of technology.
Degrease the skins with a blunt knife, scraper or scythe. To do this, the skin, taken off the tube, is pulled onto a specially made conical-shaped log, and the removed layer is placed on an equal board with a fleshy outward.
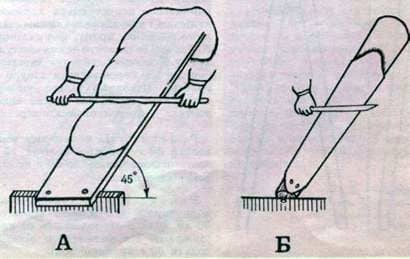
Fig. 1. Degreasing Mezdra: A – on the board; B – on a log.
Smooth movements of the scraper, delivered to the skin at an angle of 15-25 њ, scrape the skin from the back to the head, squeezing out the fat. If, after such a mechanical treatment, the skin remains greasy, it must be additionally wiped with chips dampened with gasoline (B-70 or “galoshes”) at a rate of 100 g per 1/3 buckets of chips. Remember that badly skimmed skin is heavily exposed to dressing, because fat repels the solutions of the reagents used.
Contaminated skin before dressing or canning should be washed well in cool water with usual household soap or detergent, rinse and hang for about an hour to make the glass water.
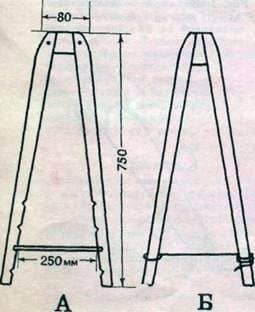
Fig.2. Types of rulers: A-sliding; B is vinous.
Preservation of the skin in a fresh-dry way is carried out by placing it on a rule and holding at 25-30 њ C (not in the sun) and 40-70% relative humidity to dry. Properly dried skin should have an elastic, elastic skin that stretches well and gets wet. To scare off moths and skins, the skin is powdered with powdered naphthalene, sodium silicofluoride. So can the skin of rabbits, nutria, dogs, cats, foxes, rabbits, muskrats, ferrets, martens and other animals.
Skins of large animals can be preserved with a kitchen salt, which is rubbed with a mash for 10-20% of salt from the weight of the skin. The salt of fine grinding (extra) is not recommended for use, as it quickly cracks, poorly soluble. If the skin is intended to be stored for a long time after canning, it is advisable to add these components to repel moths and skins. Keep the skin treated with salt, folding it inward, folding into a tube, tied with a rope and put in a cool place. Canned skins persist for several years.
Skins should be made in a separate adapted room, which is well ventilated. It is better to do this during the warm season, since the working solutions should have a temperature of 20-25 њ. To work with chemicals you need to have rubber gloves, nylon buckets, respirators, oilcloth aprons. It is convenient for processing hides to use a plastic baby bath.
Soaking the skin is done when dealing with canned skin. Soaking makes the skin elastic. Freshly soaked hide does not require soaking. It is not recommended to soak the skin in a bowl that is oxidized (galvanized buckets, tanks, copper basins). The skin should be completely covered with a solution, and not to float away, a board with a load is placed on it.
There are many recipes for preparing a solution for soaking skins. Here are two of them, simple and reliable.
1. 60 g of the kitchen salt and 3 g of zinc chloride are taken per liter of water.
2. To a liter of water, take 50 g of the kitchen salt, 30 g of borax, 2 g of crystalline carbolic acid.
The ratio of the working solution (in liters) to the mass of the wet skins (in kilograms) should be at least 5: 1. When it comes to dealing with a rotten hide from which wool falls out, formalin is added to the solution with 1 ml per liter. Soak for 1-4 days at a temperature of 20-25 њ C. The duration of soaking depends on the quality of the primary treatment, the method of preservation and the time of storage of the hide.
Mezdru, which is strongly stiffened, must be mitigated, using the method of “nazhoru”. To do this, put the skin for 1-1.5 h in a 0.3% solution of acetic acid and stir occasionally. When the masdra becomes soft, the swollen skin is put in a soaking solution and left there to complete this operation. Freshly canned skin soaks quickly and after a few hours it can be taken out of solution. Poorly subjected to soaking is not enough skim. Do not perceive water as a skin with keratinized masdra, which is formed as a result of improper accelerated drying, when the keratinized surfaces of the masdra form white areas (“bait”).
Soak “zhivtsy” alkaline enhancers, which are added to the solution of ammonium alcohol at a rate of 50 ml / l or baking soda 10 g / l. Qualitatively and quickly soaked skins, canned in kitchen salt, worse – fresh-dry preservation. If soaking is delayed, it is advisable to change the solution every 24 hours. Soaking off rotted skins, we recommend using recipe # 1 with zinc chloride, which well fixes the wool. It is not recommended to use hard water. Rigidity of water can be eliminated by boiling or adding ammonia (ammonia) alcohol (10-12 ml per liter).
Signs of the completion of soaking: Mezdra throughout the skin is soaked off uniformly, soft, stretches well in all directions; the coat on the skin holds tight.
Mezdrovaniyaenachain, when the skin is still wet. After soaking it is pulled out of the solution, hanging on a crossbar to drain water. If the fur is thick and the water is delayed, the skin should be easily shaken and beaten with a stick. Mezdrovanie – mechanical processing of a skin not very sharp knife for the purpose of isolation of hypodermic fiber and loosening of fibrous structure of the skin. This facilitates the penetration of chemicals into the skin during its manufacture.
For skinning, the hide is spread on a wooden board or a log with a skin to itself, so that the main end of the skin is at the bottom. The tail part of the skin should be fixed, pressing to the log, and processed in the direction from the tail to the head. In the area of furrowing, the skin must be stretched so that no creases are created. It is advisable to dress the oilcloth apron during the mashing. Work carefully so as not to make incisions on the skin. First, make a wide band along the spine, then unfold the skin 90 њ and the side sections, moving the knife from the spine to the sides.
In the process of furrowing from the skin it squeezes out the fat, and so that it does not come across the wool and does not stretch over the masdres, the latter is advised to always sprinkle with dry shavings or chalk. Mezdrovanie is finished, when there is no subcutaneous tissue left on the skin and it takes water well. The experienced person spends 1.5-2 hours to create calfskin.
Washing and final degreasing. Fat skins of animals such as sheep, dog, arctic fox, badger, otter and others are degreased first in a special solution, then washed. Skins without excessive fat are only washed. To prepare a degreasing solution, take 8 grams of a dining room or 5 grams of caustic soda per liter of warm water (25-30 њ C). Mezdru before degreasing it is necessary to process all skins on a surface a metal brush. The skin in the solution must float freely. If the masdra is thin and equal, then it is enough to wash the skin with your hands in such a solution. After 2-3 hours the masdra will turn white and sing under the fingers. If the solution gets brown after 1-2 hours, it needs to be replaced.
Having finished skimming, skin is rinsed in warm water and washed in a solution of laundry soap (10 grams per liter), or detergent (3 g per liter). Wiping and wringing the skin with his hands, carefully erase it to the appearance of a characteristic creaking of wool. Then the skin is rinsed in warm and cold water, hanged and beat out with a stick. The operation for skimming and washing large quantities of skins is convenient to perform using an old washing machine.
Pickering is a crucial stage, from the correctness of which the quality of the dressing, softness, elasticity and strength of the skin largely depends. Here are a few simple universal recipes for cooking an acid pickle, which enable you to mend any skin, changing only the mode of pickle.
Recipe 1. To each liter of water add 60 g of concentrated acetic acid (essences) and 40 g of kitchen salt.
Recipe 2. To each liter of water add 2-3 grams of concentrated sulfuric acid, 10 g of concentrated acetic acid and 40 g of kitchen salt.
For a kilogram of wet skins you need 5 liters of a pickle, the temperature of the solution is 25-27 њ у. Duration of pickling with periodic stirring – from 5 to 48 hours, depending on the thickness of the mezdra (see Table 1).
Tab. 1. Mode of picking skins
Type of raw material (hide) | Amount Solution For 1 kg Humid | Working solution temperature, њ у | Duration, year | Composition of solution | , g / liter | |
Cooking salt | Concentrated acid | |||||
Skins, l | Sulfuric | Acetic | ||||
Proteins | 4 | 35 | 8 | 50 | 8 | |
Foxes, otters1 | 8 | 25 | 10 | 50 | – | 12 |
Hare | 12 | FROM | 6th | 40 | 3 | – |
Kota | 8 | 35 | 6th | 35 | 3 | – |
Krol: | ||||||
Subtle | 8 | 35 | 6th | 50 | 2.5 | – |
Mean | 8 | 35 | 8 | 60 | 5 | – |
Ferret | 8 | Thirty | 12 | 80 | 12 | – |
Foxes, arctic fox, martens, | ||||||
Mink, sable, | ||||||
Frets2 | 12 | 35 | – | 80 | – | 25 |
Nutri1 | 8 | 25 | 10 | 60 | – | 12 |
Ondatras | 10 | 38 | 36 | 50 | – | 6th |
Gopher | 6th | Thirty | 6th | 40 | 4 | – |
Dogs, wolves | 8 | 35 | 10 | 60 | – | 10 |
Foal and booze | 8 | 35 | 12 | 60 | – | 20 |
Sheepskin fur | 7th | 38 | 4 | 50 | 2.5 | – |
Fur coat | 5 | 37 | 14 | 40 | 4 | – |
A lamb, a goat, | ||||||
Smiles3 | 10 | 38 | 36 | 50 | – | 9 |
Strap | 10 | 35 | 10 | 40 | – | 6th |
1 if necessary | Repeated in the same regime to the formation of “sushinka” | |||||
2 treatment is carried out 3-4 | Times 2 | Hours with “lying” in breaks for 4 hours | ||||
3 acetic acid was added portionwise: first | 1g / l, through | 2 and 8 hours | Another 1 g / l and through | 24 hours 6 | G / l | |
Pickering is stopped when the masdra acquires the consistency of a tight dough, and when it is squeezed with fingers (large and indexed) a “dryer” is formed – a dry, light lozenge of diamond-shaped shape that forms on the flesh of the skin that was in the pickle after it was squeezed with fingers. When the constriction is stopped, the tubercle gradually becomes moist, leveled and disappears. After the end of the pickling, the skin is slightly squeezed, rolled into a roll with a flesh to the flesh, wrapped with a wet burlap and allowed to “lie down” for 10-12 hours at room temperature. After “lying down” the skin is carefully rinsed in water at room temperature, shaken several times and hung to make the glass water.
Neutralization. The acid, which is partially left after the pickling, must be neutralized, otherwise the tanned skin will lose its strength with time. Neutralize with a 5% solution of sodium hyposulfite (50 grams per liter), which is used in the photo session. Apply only a freshly prepared solution in relation to the mass of the wet skins (2: 1). Immersed in a solution of hyposulfite skin for 20-C mines vigorously crushed hands, then left in solution for 2 hours. During neutralization, hydrogen sulphide with an unpleasant smell is released, and therefore the rooms must be ventilated. After neutralization, rinse the skin again and hang it to make the glasses water.
Tanning. Skins without tanning in case of their moistening and under the influence of low temperatures coincide, become inelastic, firm. For tanning use different chemicals, as well as folk remedies – a decoction of oak bark. Of the chemicals most often use chromium-potassium and aluminum-potassium oxalis, chromium oxide, formalin. The best results are given by chromium compounds. In the process of tanning it is important to periodically move the skins in the solution. Here are a few universal recipes that can be used to smear the skin.
Recipe 1. For each liter of water add 40 g of kitchen salt and 15 g of aluminum-potassium or 20 g of chrome-vanadium sorrel.
Recipe 2.1 kg of dry oak bark is boiled in 5 liters of water for 30 minutes. The broth is cooled and filtered. For each liter of broth add 30 g of salt.
Tanning lasts 4-12 hours at a solution temperature of 20-25 њ C. A kilogram of skins consumes 2 liters of solution (see Table 2).
Table 2 Mode of tanning skins
View | Amount | Tempe – | Continuing | Composition of the solution, g / l | |||||
Solution | Circuit | ||||||||
Raw materials | For 1 kg | Workers’ | Vitality, | Kitchen | Oxide | Hypo – | Soda | Chromo – | Urotropy – |
(skin) | Salt | Chrome | Sulfite | Calci – | Potassium | Hexamethylene – | |||
Humid | Th raster | Hour | |||||||
Skins, l | Thief, њ у | Sodium | The new | Alum | Thiotetra-nil | ||||
Proteins | 7th | Thirty | 2.5 | Thirty | 0.45 | ||||
Foxes, see | 8 | 25 | 12 | 60 | 1.0 | – | 0.5 | – | – |
Hare | 12 | Thirty | 10 | 40 | 0.9 | – | 0.5 | – | – |
Kota | 8 | 35 | 12 | 50 | 0.9 | 8 | 2.0 | – | – |
Krol: | |||||||||
Subtle | 8 | 35 | 6th | 50 | 0.9 | 8 | 0.5 | – | 1 |
Mean | 8 | 35 | 12 | 50 | 0.9 | 10 | 1.0 | 8 | 1 |
Ferret | 10 | 28 | 10 | 40 | – | – | – | 8 | – |
Foxes, arctic fox, martens, mink, | |||||||||
Sables, coins | 12 | 35 | 6th | 60 | 4.0 | – | – | – | – |
Nutria | 8 | 35 | 12 | 40 | 0.9 | 10 | 1.0 | 8 | 1 |
Ondatra | 10 | 35 | 6th | Thirty | 0.9 | 8 | – | – | – |
Gopher | 8 | Thirty | 10 | 40 | 0.9 | – | 1.5 | – | – |
Dogs, wolves | 8 | Thirty | 13 | Thirty | 1.8 | – | 1.0 | – | – |
Foal and booze | 8 | 35 | 12 | 40 | 2.5 | – | 0.5 | – | – |
Sheepskin fur | 7th | 38 | 6th | Thirty | 1.2 | – | 0.5 | – | 1 |
Fur coat | 5 | Thirty | 17th | Thirty | 2.0 | – | 1.5 | – | – |
The lamb, the goat, the littles | 10 | Thirty | 10 | 40 | 0.9 | – | – | – | – |
Strap | 10 | Thirty | 10 | 50 | 0.9 | 10 | 1.0 | – | – |
After tanning, rinse the skin several times in water at room temperature and hang to dry. Then, still quite wet skin carefully examine from the side of the skin and if there are deep or through damage, sew them with a strong thread. Now it needs to be dried. The skin, removed by a tube or stocking, is dried on a rule, and removed by a layer – is stretched on a plywood, wooden shield or on a frame. Stretch the skin as much as possible on the side with a crease upward. Slippery wet skin is better to stretch with the help of pliers. The extracted skin should not have wrinkles. Fix the skin in a stretched position with the help of nails, which are clogged, leaving the edge of the masdra by 10 mm and one from the other by 10 cm. Dry the skin at an ambient temperature of 25-30 њ C in a room that is well ventilated. In the sun and near the stoves, fireplaces, batteries and reflectors can not be dried. Normally dried mezdra is similar to medium-density cardboard.
Moistening is necessary in order to become softer than the skin of the dried skins and thus prepare it for the next treatment – “breaking down”. If the skin is thin, then you can not humidify, but immediately proceed to “breakdown.” In this case, the skin should be slightly moist. Moistening is done by wetting – smearing with 1-3% aqueous solution of carbolic acid with a brush or putty. Then the skin is fused along the spine twice deep inside, it is rolled into a roll, which is wrapped with moist sackcloth, put in a cellophane bag and left for a day under yoke. After moistening, the masdra becomes soft all over the surface and dries quickly. When it becomes almost dry, proceed to the “breakdown”.
Fig. 3. The device for “breaking” the skin: A – ring; B – metal fork; B – table.
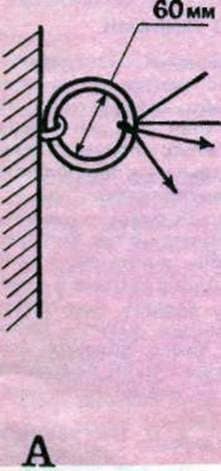
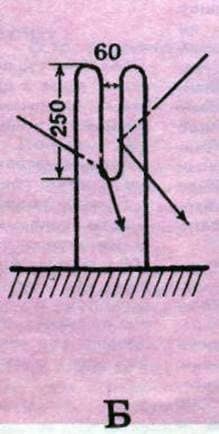
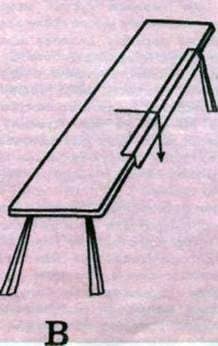
The breakdown is necessary to soften the skin. It is stretched by the surface of the mezdra through special devices: a metal ring, a fork or the edge of the table, upholstered in metal. First, the skin is stretched on the spine from the tail to the head, then from the spine to the sides and finish “breaking” the edges. Small skins can be “smashed”, stretching them with their hands without any adaptations. “Smash” the skin should be a fairly long time, until the masdra becomes soft and supple.
Stripping (the last operation of dressing) provides the surfaces of the furrow of uniformity and equality. The hide is placed on a razor-sharp log covered with two or three layers of sacking, and sandpaper or pumice is processed with a sheath until it becomes milky and equal. If you use sandpaper, then it is better to wrap a block of styrofoam, and if pumice, then on hand put on an old mitten.
Immediately after stripping the skin must be greased with grease, which will preserve its elasticity and prevent drying out. Fat emulsion is prepared from the calculation: household soap 25 grams, castor oil (castor oil) 20 g and 1 g borax per 1 liter of water. First bring water to a boil and dissolve in it soap, then add castor oil and brown. Castor oil can be replaced with pork melted fat (30 g). Such an emulsion is lubricated once with the skin of the skin to dry completely. After lubrication, the skin is slightly beaten with a stick (a small shake), the hair is combed with a scallop or metal brush, first sparse, and then thick. Now the skin is ready, and it can be used for its intended purpose.
Сколько сиропа давать пчелам. Простокваша с медом.
Useful tips for the amateur beekeeper